Artificial intelligence (AI) is one of those terms that gets thrown around a lot these days. It´s everywhere – your phone, your favorite streaming service, even in the algorithms deciding what ads you see. But let´s be real: most people don´t fully understand what AI is, where it came from, or what it actually does. If you are nodding along right now, don´t worry – you are not alone. In this article, we are cutting through the jargon and breaking it all down in plain, easy-to-understand terms.
The Origin of AI: From Humble Beginnings to World Domination
To understand what AI is today, we need to rewind a bit. The idea of machines that could “think” or mimic human intelligence isn´t new – it´s been around for centuries. Philosophers as far back as the ancient Greeks toyed with the concept. But it wasn´t until the mid-20th century that AI started to become more than just science fiction.
The Role of Alan Turing: The father of AI
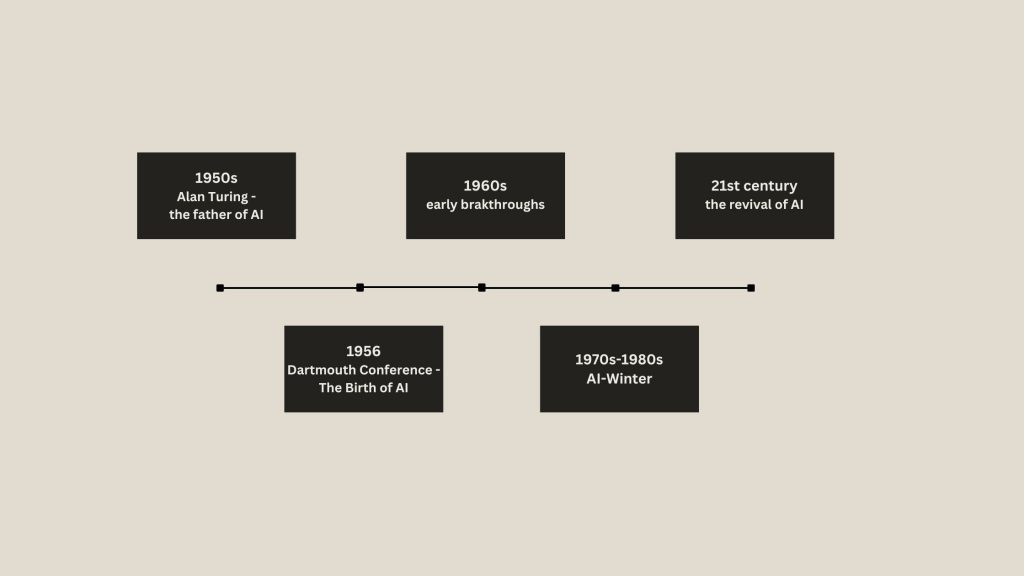
A pivotal figure in the origin of AI is Alan Turing, the British mathematician and computer scientist. In 1950, Turing introduced the concept of machine intelligence in his groundbreaking paper, “Computing Machinery and Intelligence”. He posed a simple yet revolutionary question: Can machines think? To explore this, Turing proposed the famous Turing Test, a method to determine whether a machine can exhibit human like intelligence by engaging in natural conversation indistinguishable from human´s. While modern AI has evolved beyond the Turing Test, his work laid the theoretical foundation for what we now call artificial intelligence.
1950s: The Birth of AI
The term “artificial intelligence” was officially coined in 1956 at a conference at Dartmouth College, led by computer scientist John McCarthy. Back then, the goal of AI was pretty straightforward: create machines that could think and learn like humans. The first attempts were simple – playing games like chess and solving basic mathematical problems.
The Early Breakthroughs
One of the first big moments in AI came in the 1960s, with programs like ELIZA, an early chatbot that could simulate conversations. Sure, it wasn´t perfect – it mostly repeated what you said back to you – but it was a step in the right direction.
The AI Winter
But progress wasn´t smooth. By the 1970s and 1980s, enthusiasm for AI had cooled. Why? Because early AI systems just didn´t live up to the hype. Funding dried up, and it seemed like AI was destined to be a niche topic for researchers rather than a game-changer for humanity.
The Revival
Fast-forward to the 21st century, and AI has made a huge comeback. Thanks to advancements in computing power, data availability, and algorithms, AI is now everywhere – from the smartphone that you use everyday to the systems running self-driving cars.
Ok, but what the f*** is AI, really?
At it´s core, artificial intelligence is about creating machines that can perform tasks that usually require human intelligence. Think of it as teaching a computer how to “think” and “learn” in specific ways.
There are a few key concepts that help explain how AI works:
Machine Learning (ML): The Brain Behind AI
Machine Learning is a type of AI that allows systems to learn from data. Instead of programming a machine with every possible rule (which would be impossible), we feed it data and let it figure out patterns on its own. For example: Show an AI 10.000 photos of cats and dogs. It “learns” what makes a cat a cat and a dog a dog. Now it can correctly identify whether a new photo is a cat or a dog.
ML powers things like Netflix recommendations, spam filters, and even your social media feeds.
Neural Networks: Mimicking the Human Brain
Neural networks are inspired by the way human brains work. These are algorithms designed to recognize patterns, make decisions, and even predict outcomes. They are great for complex tasks like image recognition (e.g. facial recognition on your phone) or natural language processing (e.g. chatbots like ChatGPT).
Deep Learning: AI on Steroids
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses massive neural networks with many layers. This is what powers the most advanced AI systems today, like self-driving cars or voice assistants. Deep learning requires a lot of data and computing power, which is why it´s become more popular in recent years as technology has advanced.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Making AI Understand Us
NLP is what allows AI to understand and respond to human language. It´s why you can ask Siri or Alexa a question, and the (usually) understand you.
So, What Can AI Actually Do?
AI is everywhere, and its applications are as divers as they are fascinating. Here are a few examples:
- Healthcare: AI helps doctors diagnose diseases faster, develop personalized treatment plans, and even predict outbreaks.
- Finance: Banks use AI to detect fraud, automate customer service, and make smarter investment decisions.
- Entertainment: From Netflix recommending your next binge-worthy series to AI-generated music and art, the creative applications are endless.
- Transportation: Self-driving cars? Yup, AI is at the wheel.
- Customer Service: Chatbots and virtual assistants are powered by AI, handling everything from booking appointments to answering FAQs.
What AI isn`t
There is a lot of hype around AI, but it´s important to separate fact from fiction.
AI Isn´t Sentient
Despite what sci-fi movies would have you believe; AI does not have feelings or consciousness. It´s not self-aware, and it´s not plotting to take over the world (at least, not yet).
AI Doesn´t “Think” Like Humans
AI is great at specific tasks (e.g. recognizing faces, translating languages), but it doesn´t have general intelligence like humans do. For example, an AI that´s amazing at playing chess won´t know how to play poker.
Why Does AI Matter?
AI is more than just a buzzword. It´s changing the way we live, work, and interact with the world.
Here´s why it´s such a big deal:
- Efficiency: AI can handle repetitive tasks faster and more accurately than humans.
- Innovation: It´s enabling breakthroughs in fields like medicine, science, and technology.
- Accessibility: AI-powered tools are making education, healthcare, and information more accessible to people around the world.
The Risks and Challenges
Of course, AI isn´t perfect. There are still plenty of challenges and risks to consider:
- Bias: AI systems are only as good as the data they´re trained on. If the data is biased, the AI will be too.
- Privacy: AI often relies on huge amounts of personal data, which raises concerns about how that data is collected and used.
- Job displacement: Automation powered by AI could replace some jobs, although it´s also creating new ones.
So, What´s Next for AI?
The future of AI is exiting – and a little uncertain. We are already seeing advancements in areas like: Generative AI (creating new content, like art and writing), AI ethics and regulation (ensuring AI is used responsibly) and AI-human collaboration (working together to solve big problems).
Final Thoughts
AI might seem like a complicated, futuristic concept, but at its core, it´s all about using technology to solve problems and improve our lives. Whether it´s helping doctors save lives, making your Netflix recommendations eerily accurate, or just answering your random questions, AI is shaping the world around us in ways big and small.
So, the next time someone asks, “What the f*** is AI?”, you´ll have the answer – and hopefully, it won´t seem so intimidating anymore.
Stay curious, stay informed, and let´s keep exploring the fascinating world of AI together.
This post was written with the help of different AI tools.
Recommended Read and Listen
Disclaimer: The links provided on this blog lead to external websites that are not under my control. I do not guarantee the accuracy, reliability, or content of these external sites. Visiting these links is at your own discretion and risk.